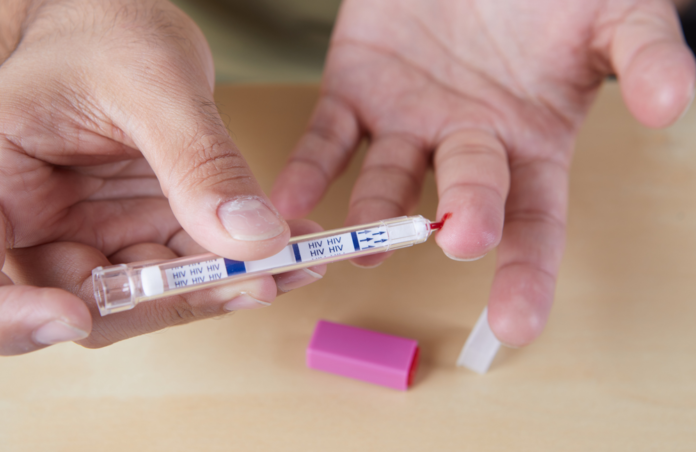
Taking a non reactive HIV test can be a great way to find out whether you have HIV. However, the results don’t always mean that you don’t have HIV. The reason for this is that there are many factors that affect the results of a non reactive HIV test. These factors include the length of time you have been infected, the amount of anti-bodies you have, and whether you have been treated or not. Here we will discuss about most important question : what does non reactive hiv test mean ?
Also Read: colon broom reviews
Positive results don’t always mean you don’t have HIV
Getting a positive HIV test result isn’t the only sign of infection. You may also be exposed to the virus by sharing contaminated needles, sex, or transfusion of contaminated blood. In these cases, you may be able to pass it on to others. Using condoms properly will help prevent transmission of HIV.
The best way to avoid getting HIV is to avoid sex and use condoms. If you do get infected, there are ways to treat the virus and prevent further damage to your body. The most effective way to control HIV is to take antiretroviral drugs. Antiretroviral therapy works by suppressing the virus and keeping it from damaging your immune system. It is recommended for all HIV patients.
There are a number of different tests available. The standard blood test can detect antibodies to HIV in about 23 to 90 days after infection. Some tests, such as the nucleic acid test, look for the actual virus in your bloodstream. Nucleic acid tests are most effective if you have been exposed within the past few weeks. They can be done at home, but you should get a second opinion from a health care provider before doing it yourself.
There are also rapid tests that can provide results in less than a half an hour. These tests are available at community clinics and at home. Some tests, such as the rapid oral fluid test, are the most likely to give a false positive result. This test is done by swabbing the gums with a home test kit. The test takes about 20 minutes to complete. The test isn’t very accurate, but it’s one of the best ways to check if you have the virus.
Other tests are more accurate. The nucleic acid test can detect the presence of the virus in your bloodstream up to 33 days after you have been infected. The best way to find out if you have the virus is to get tested, but if you have been infected, the nucleic acid test is the only way to know for sure.
Another good way to know if you have the virus is to take antiretroviral drugs. These medications help to lower the amount of the virus in your body, and this will decrease your chances of developing AIDS.
If you do test positive for HIV, you may need to go to a doctor or other health care provider to get a follow-up test. This is especially important if you live in a high-risk community. You can also contact your local health department to get the test you need.
You should also try to avoid sharing needles and using condoms properly. This may prevent the spread of the virus to your partner. You may also have to take a number of different medicines to treat your viral infection. You may even need to have radiation or chemotherapy.
Time between HIV infection and the production of antibodies
During an HIV infection, a person’s immune system slowly weakens. As a result, the person is prone to opportunistic infections, which can be serious. In addition, HIV causes a condition called acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), which increases the risk of certain cancers.
The time between HIV infection and the production of antibodies is referred to as the window period. It can be as long as six months. This period is important because it gives the person time to develop antibodies, which are a key component of protective immunity. In addition, the time between infection and antibodies can vary significantly, depending on the individual. However, most people have antibodies within two to six months of infection.
The first antibodies that develop during an acute HIV infection are a subset of antibodies called early neutralizing antibodies. These antibodies are not effective in blocking the current HIV strain, but they are effective in providing a small amount of protection from future infections. These antibodies appear around two weeks postinfection. However, the time between HIV infection and the production of antibodies can vary from person to person. Some people can take as long as three months, while others have antibodies developed as early as three months after exposure.
The time between HIV infection and the formation of a neutralizing antibody is important because these antibodies can put pressure on the virus and prevent the virus from entering the body. These antibodies can also be effective in protecting a person from re-infection. The time between HIV infection and the production of a neutralizing antibody can also vary depending on the strain of HIV. However, most people will develop a neutralizing antibody within two months of infection.
Antibodies can also help to detect HIV infection. These antibodies are particularly detectable in the plasma, where they can help to detect HIV infection. However, they are not as useful as a NAT or an antigen test, which are used to detect HIV in the blood. A NAT looks for the HIV virus in the blood, while an antigen test looks for antibodies on the surface of the HIV virus. NATs look for the p24 antigen, which is a component of the HIV virus.
The time between HIV infection and the creation of antibodies is important because it is the only way to detect the virus. This process is the first step in a person’s AIDS. Fortunately, this process is treatable. If a person is positive for HIV antibodies, they can begin treatment right away. However, if a person is negative for HIV antibodies, they should continue to take preventive measures. This includes continued counseling to teach them how to protect themselves from infection and from infecting others.
During an HIV infection, a person’s white blood cells drop and their T-cell count decreases. The immune system eventually weakens, and HIV begins to destroy its own cells. This is called “acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.” This condition increases the risk of certain cancers and increases the risk of death.
False positive results
Having a false positive result on a non reactive HIV test is an extremely rare situation. However, the emotional and health implications of this situation are significant. In addition to causing unnecessary antiretroviral treatment, it can lead to complications and side effects. It can also damage the public’s trust in the healthcare system.
In the United States, there are 1.2 million people living with HIV. In addition to HIV, people can also have other health conditions that can lead to a false positive result on a non-reactive HIV test. These include autoimmune disorders, pregnancy, and other viral infections.
The main causes of false positive results on a non-reactive HIV test include mislabeling, technical errors, or facility issues. Other reasons for a false positive result include vaccination, ameloblastoma, and hypergammopathy of the hematologic malignancy.
In the United States, there are two types of HIV tests. A rapid point-of-care test and a blood-based test. Both can detect HIV, but the blood-based test is more accurate. In addition, a blood-based test has a longer window of time to detect HIV. This is called the positive predictive value.
There is a higher chance of a false positive result with a rapid point-of-care HIV test than with a blood-based test. However, a small percentage of people who test positive on a rapid point-of-care HIV antibody test may actually be HIV negative. The CDC recommends that a person who tests positive on a rapid point-of-care test retest 45 days later to confirm that he or she is HIV negative.
False reactive serology is caused by polyclonal activation during systemic infections, vaccination, mislabeling, on-instrument contamination, transient cross-reactivity, or other biological factors. It is also possible for a person to have a false reactive serology result if he or she has been infected with SARS-CoV-2.
In the United States, the probability of a reactive HIV serological result being correct is 28.5%. In a community with a high HIV prevalence, there is a lower probability of a false reactive result. However, the likelihood of a false reactive HIV test results being correct increases as the prevalence of HIV decreases.
In the United Kingdom, a 99.5% sensitivity test is used to diagnose HIV. Several examples of positive predictive value are given for tests with 99.5% sensitivity and specificity. If you have a reactive HIV test result, you may be contacted by your local health department. In these cases, you should seek medical care. Having a reactive HIV test result can lead to unnecessary antiretroviral treatment.
In addition to reactive HIV test results, there are also false positive fourth-generation screening tests. These tests have been associated with tuberculosis, autoimmune disorders, and malignancies. However, a number of falsely reactive fourth-generation screening tests have been reported in association with pregnancy and Epstein-Barr virus infection.