Electric bikes (or e-bikes) are slowly becoming the norm as sustainability initiatives take route in cities and local communities. Many prefer this electric vehicle for being a more affordable and cleaner means of traveling than using a car. They’re also easier to maintain and allow you to cycle as exercise.
Moreover, when it comes to an e-bike’s make, each one has different mechanical parts that work together cohesively to make it function. Thus, if you’re starting to learn about your bike, it will benefit you to know how every component fits into its overall structure to make it work.
Here are four things you should know as an e-bike beginner:
- E-Bike Modes
Every e-bike is classified according to how power accelerates itself, including throttle or pedal assist. The throttle concerns the display devices integrated into the bike’s system and mounted onto the handlebars like a motorcycle. Meanwhile, the pedal assist is about supplying you with more power as you peddle. Both modes use the type of motor built into their frame.

Thus, as a beginner e-biker, if you choose one with a throttle system, like those on Chargebikes, you can expect to cruise along with minimal effort. This mode also comes with settings where you can adjust the amount of power produced by the motor to move at the speed of your choice. Pedal assist, on the other hand, offers you the chance to be more involved in creating power through pedaling. However, you can utilize the assist function to take over most of your manual cycling if you need to ease the strain on your legs when rising over an incline.
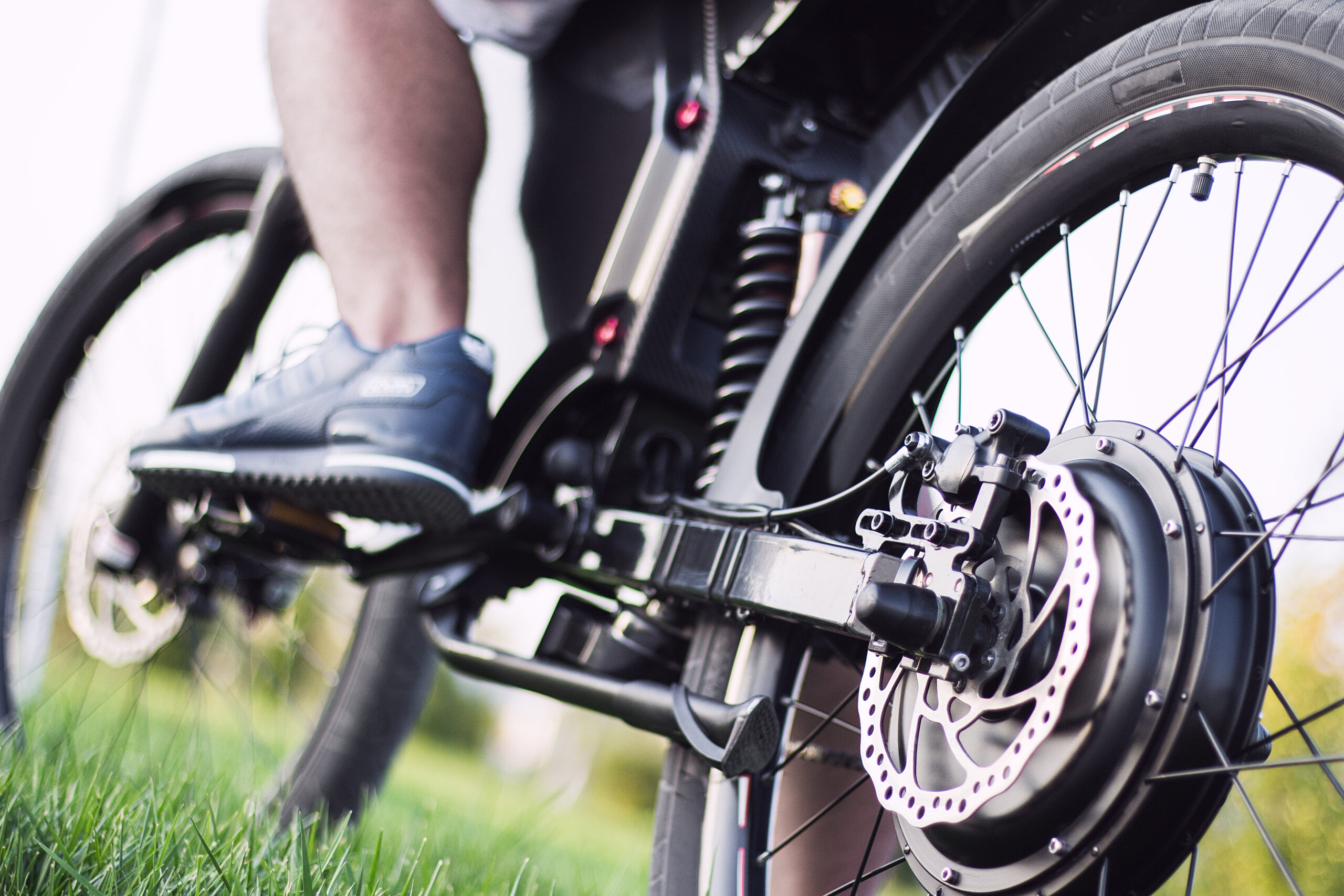
- Motors
The motors are essentially the engine system of an e-bike that uses electrical energy to keep it moving. This sets it apart from traditional bicycles that operate solely on gears and pedals. They are an essential consideration for e-bike beginners because the type of motor your bike has will determine its performance. They also affect how suitable the bike is in various environments.
There are two types of e-bike motors—the mid-drive and hub drive motors, positioned either at the front, center, or back of the bike. The mid-drive motor transfers power to the back wheel and bike pedal gears to make it efficient for cycling uphill during off-road and mountain biking terrain. Meanwhile, the hub drive is directly connected to the wheel from the rear to create balanced weight diffusion and a seamless, smooth riding experience over soft precipitation.
- Speed Control
Sensors control the speed of an e-bike. These display the speed at which you’re moving (cadence sensors) or detect the motor’s rotation energy output to moderate your speed during pedal assist mode (torque). The cadence sensors can work manually by switching through the speed levels from low and coasting to fast and intense when you’re using the e-bike pedaling as part of a fitness routine.
On the other hand, the torque sensor usually happens automatically as this technology is designed to equalize your peddling performance with the motor’s power. Due to the advanced nature of torque mechanisms, it’s usually in high-priced and prestigious e-bikes currently. Regardless, both of these controls require you to be familiar with local speed limitations and regulations to operate them and keep you compliant with the law.
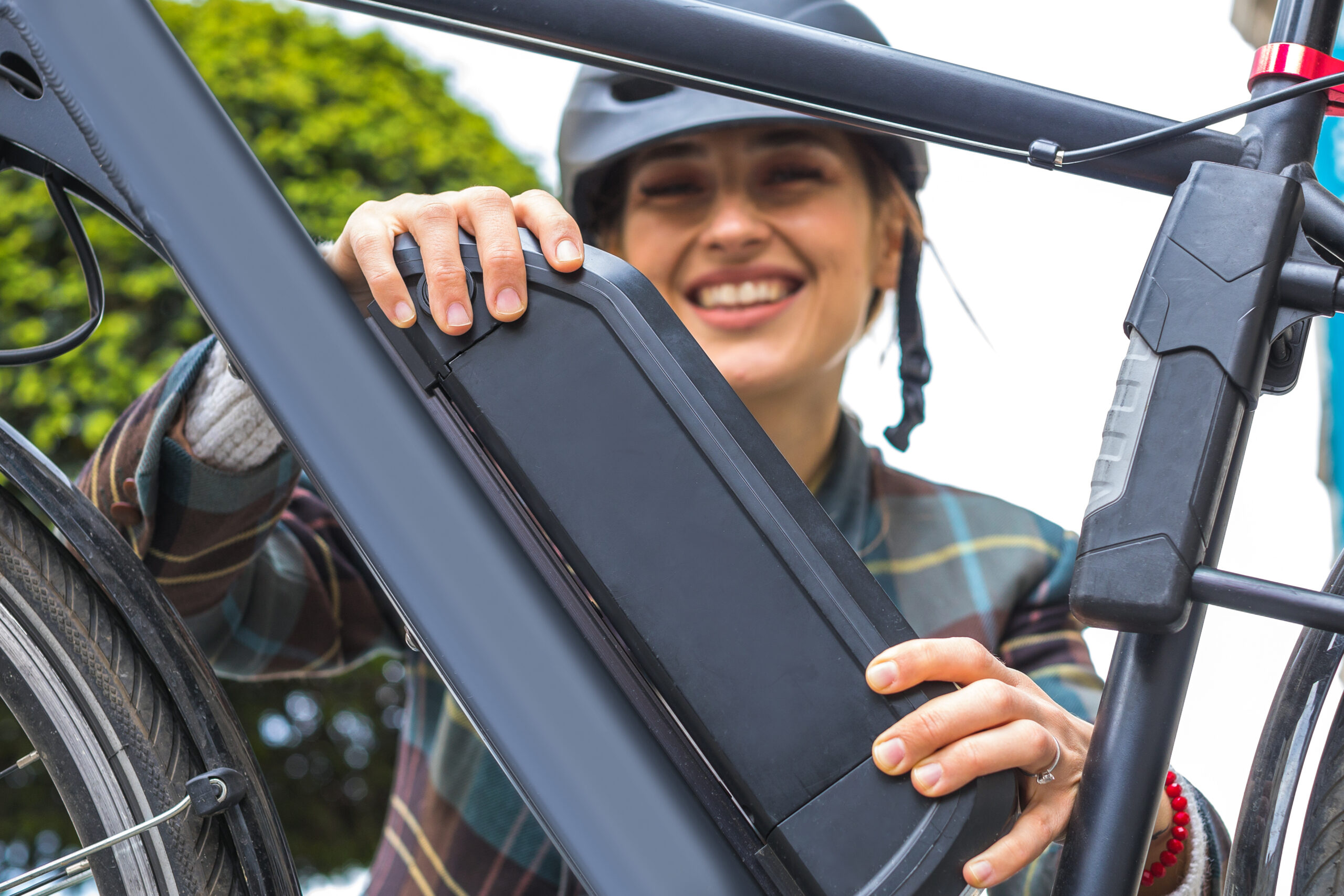
- Battery
If the motor is considered the engine of an e-bike, then the battery is its fuel source. This lithium iron-based battery pack conducts the electrical flow used by the motor to power up the bike. Because it’s electrical, you’ll need to charge it ideally after a long-distance ride, depending on its lasting capacity and how much power you use to move you over challenging conditions.
Most e-bike batteries are typically made lightweight with a voltage capacity of 36–48V of power that can take you about 40 miles with a 100% battery charge. Some bikes have a battery capacity of 48V to navigate mountains and steep-sloped terrain better, such as San Francisco’s rolling hills.
Conclusion
E-bikes work in synergy with the combined mechanizations of the motor, battery, mode, and speed controllers. It all begins with the battery creating the electrical voltage needed to bring the motor to life. Once achieved, you can customize your ride and speed according to your preference as a beginner biker.
Remember to adhere to speed limitations, traffic laws, and road allowances in the areas you’ll be riding. After all, the best way to learn how your e-bike works with the specs of its model is to try it out in a safe setting.